Have you ever spent months grinding at the gym only to see the same reflection in the mirror every morning? It feels like you are pouring water into a bucket with a hole in the bottom. Here is the thing: your training might be perfect, but without a structured muscle gain diet, your body simply lacks the raw materials to build new tissue. Muscle growth does not happen while you are lifting weights. It happens when you are resting, provided you have fueled your recovery with the right nutrients. This 7-day muscle gain diet plan is designed to bridge the gap between your hard work in the gym and the visible results you deserve.
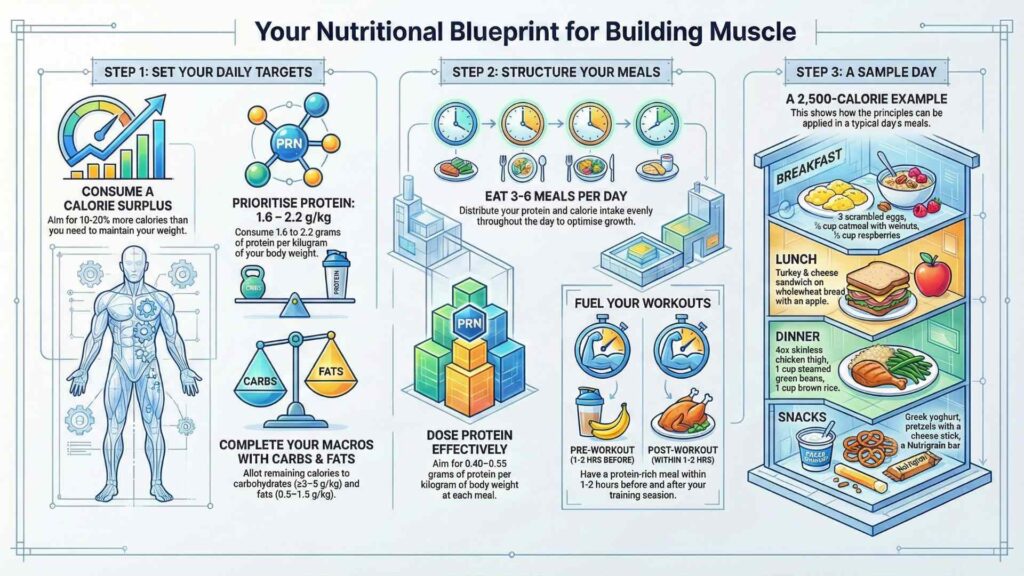
Table of Contents
- 1 The Biological Foundation of Hypertrophy
- 2 Calculating Your Personal Muscle Building Requirements
- 3 Macronutrient Distribution for Hypertrophy
- 4 7-Day Meal Plan for Muscle Growth: The Detailed Schedule
- 5 Best Protein Sources for Mass
- 6 Bulking on a Budget: How to Gain Mass Without Breaking the Bank
- 7 Muscle Recovery Foods: Why Your Diet Doesn’t End at the Gym
- 8 Common Muscle Building Mistakes for Beginners
- 9 Understanding “Newbie Gains”: What to Expect in Your First Year
- 10 FAQs: Mastering Your Muscle Gain Diet
- 11 Conclusion: Taking the First Step Toward Your Gains
The Biological Foundation of Hypertrophy
To understand how a 7-day meal plan for muscle growth works, we must first look at the science of Muscle Protein Synthesis (MPS). Skeletal muscle is more than just a tool for movement; it is a vital reservoir of amino acids used by the body during times of stress, such as injury or illness. To force the body to add to this reservoir, we must create an anabolic environment where protein synthesis exceeds protein breakdown.
The Leucine Trigger and mTOR Activation
The most critical component of this process is an amino acid called leucine. Think of leucine as the chemical “on” switch for muscle growth. When you consume high protein foods rich in leucine, it activates the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway. Research indicates that you need roughly 3 to 4 grams of leucine per serving to maximize this response. This is why the quality of your protein matters just as much as the quantity.
| Protein Source | Leucine per Serving (Approx) | Bioavailability |
| Whey Protein Isolate | 3.5 g | Very High |
| Chicken Breast (150 g) | 2.8 g | High |
| Large Egg | 0.6 g | High |
| Soy Protein (30 g) | 2.2 g | Medium-High |
| Lentils (1 cup) | 1.3 g | Medium |
What this really means is that a muscle gain diet for beginners should prioritize complete proteins that offer a full amino acid profile. You can find more personalized guidance on balancing these nutrients by consulting experts at(https://dietdekho.com/form/).
The Role of Energy Balance and Calorie Surpluses
You cannot build a house without enough bricks, and you cannot build muscle without enough energy. A common mistake is focusing only on protein while ignoring total calories. To gain lean mass, you generally need to consume 10% to 20% more calories than your body burns to maintain its current weight. This is known as a caloric surplus. For a 150-pound individual, this typically translates to an intake of 2,500 to 2,800 calories per day.
Calculating Your Personal Muscle Building Requirements
Before starting your weekly muscle building menu, you need to know your numbers. Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) is the sum of your basal metabolic rate and the energy you burn through activity.
Understanding the Surplus Math
A modest surplus of 250 to 500 calories per day is ideal for a clean bulking meal plan. While “dirty bulking”—eating anything in sight—might lead to faster weight gain, it often results in excessive fat storage that is difficult to lose later.
The math for lean gains looks like this: TDEE+300 kcal=Target Daily Intake
| Activity Level | Multiplier | Description |
| Sedentary | 1.2 | Little to no exercise |
| Lightly Active | 1.375 | 1-3 days of exercise/week |
| Moderately Active | 1.55 | 3-5 days of exercise/week |
| Very Active | 1.725 | 6-7 days of heavy exercise/week |
If you follow these guidelines, you can expect to gain 0.25 to 0.5 pounds per week. This controlled growth ensures that the majority of the weight you put on is functional muscle rather than body fat.

Macronutrient Distribution for Hypertrophy
A hypertrophy diet plan relies on a specific balance of protein, carbohydrates, and fats. Let’s break it down into manageable percentages.
Protein: The Building Block
Protein should make up roughly 25% to 35% of your total calories. According to Harvard Health, the “protein package” matters; you should choose lean sources to avoid excess saturated fats. For active individuals, the NIH recommends 1.2 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight.
Carbohydrates: The Training Fuel
Carbohydrates are your primary energy source for lifting heavy weights. They fill your muscles with glycogen, which prevents premature fatigue. Aim for 45% to 60% of your calories from carbs, focusing on complex sources like oats, brown rice, and sweet potatoes.
Fats: The Hormonal Regulator
Healthy fats are essential for maintaining testosterone levels and overall cellular health. These should account for 15% to 25% of your diet. Focus on monounsaturated fats found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil.

7-Day Meal Plan for Muscle Growth: The Detailed Schedule
This menu is structured for a 2,800-calorie target. If your needs are higher or lower, you can scale the portion sizes accordingly.
Day 1: The Foundation
Monday is about setting the tone with consistent, high-quality meals.
- Breakfast: Three scrambled eggs, one cup of oatmeal with berries, and a glass of milk.
- Snack 1: Greek yogurt with a handful of almonds.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken breast (150 g), one cup of quinoa, and steamed broccoli.
- Snack 2: A protein shake and a medium banana.
- Dinner: Baked salmon, a large sweet potato, and green beans.
- Evening Snack: Cottage cheese with sliced pineapple.
Day 2: The Micronutrient Boost
Variety prevents nutrient deficiencies and keeps the diet sustainable.
- Breakfast: Whole-wheat toast with peanut butter and sliced bananas.
- Snack 1: Two hard-boiled eggs and an orange.
- Lunch: Turkey wrap on a whole-wheat tortilla with hummus and bell peppers.
- Snack 2: Cottage cheese with a few walnuts.
- Dinner: Lean beef stir-fry with mixed vegetables and one cup of brown rice.
- Evening Snack: A casein protein shake mixed with water.
Day 3: Plant-Based Integration
Even if you eat meat, adding plant proteins increases fiber and improves gut health.
- Breakfast: Protein pancakes topped with fresh strawberries and honey.
- Snack 1: A handful of pumpkin seeds and an apple.
- Lunch: Lentil soup with a side of whole-grain bread and a salad.
- Snack 2: Greek yogurt with granola and blueberries.
- Dinner: Baked cod with lemon, wild rice, and roasted asparagus.
- Evening Snack: A small bowl of mixed nuts.
Day 4: Mid-Week Power
Focus on high-carb meals around your training session to sustain intensity.
- Breakfast: Oatmeal mixed with almond milk, chia seeds, and a scoop of protein powder.
- Snack 1: Sliced turkey breast and a few carrot sticks.
- Lunch: Chicken salad with mixed greens, avocado, and olive oil dressing.
- Snack 2: A protein shake and a medium pear.
- Dinner: Pork tenderloin with roasted Brussels sprouts and a baked potato.
- Evening Snack: A glass of low-fat milk.
Day 5: The Mass Gainer
Friday is about ensuring you don’t fall into a caloric deficit as the weekend approaches.
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with spinach and mushrooms on whole-grain toast.
- Snack 1: Beef jerky and a few walnuts.
- Lunch: Grilled shrimp over brown rice with steamed broccoli.
- Snack 2: Greek yogurt with sliced peaches.
- Dinner: Lean steak, a baked potato, and a side salad.
- Evening Snack: Cottage cheese with a drizzle of honey.
Day 6: Weekend Loading
Use the extra time on the weekend to enjoy diverse flavors.
- Breakfast: A powerhouse smoothie with spinach, banana, almond milk, and protein powder.
- Snack 1: Hummus with raw veggie sticks.
- Lunch: Black bean and corn salad with diced tomatoes and avocado.
- Snack 2: A protein bar and an apple.
- Dinner: Baked salmon with a quinoa and spinach salad.
- Evening Snack: A handful of almonds.
Day 7: Preparation for the Week Ahead
Use Sunday for meal prep while keeping your nutrition tight.
- Breakfast: French toast made with whole-wheat bread and topped with fresh berries.
- Snack 1: Two hard-boiled eggs and an orange.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken Caesar salad with low-fat dressing.
- Snack 2: A protein shake and a banana.
- Dinner: Stir-fried tofu with mixed vegetables over brown rice.
- Evening Snack: A cup of cottage cheese.
Best Protein Sources for Mass
Not all protein is created equal when you are looking to pack on size. Animal proteins are generally more efficient for muscle gain because they are “complete” proteins.
Animal-Based Proteins
Chicken breast is a staple because it is incredibly lean, providing about 31 grams of protein per 100 grams. Lean beef provides extra benefits, including iron, B vitamins, and natural creatine. Fish like salmon and tuna are rich in omega-3s, which help reduce muscle inflammation after a heavy lifting session.
Plant-Based Proteins
For those on a meatless diet, soybeans and tofu are the strongest contenders. They contain all nine essential amino acids. Quinoa and lentils are also fantastic because they provide both protein and the complex carbohydrates needed for energy.
| Food Category | Recommended Sources | Protein Density |
| Poultry | Chicken, Turkey | High |
| Seafood | Salmon, Tuna, Shrimp | High |
| Dairy | Greek Yogurt, Cottage Cheese | Medium-High |
| Plant-Based | Soy, Lentils, Chickpeas | Medium |
| Grains | Quinoa, Oats, Farro | Low-Medium |

Bulking on a Budget: How to Gain Mass Without Breaking the Bank
A common myth is that bodybuilding nutrition is only for the wealthy. What this really means is that you need to be smart about your shopping list.
Affordable Protein Staples
Buy in bulk whenever possible. Eggs are perhaps the most cost-effective protein source on the planet, with each egg offering about 7 grams of protein. Canned tuna is another budget-friendly option, though you should limit intake to once or twice a week to avoid mercury exposure. Legumes like dried beans and lentils are incredibly cheap and provide a double-punch of protein and fiber.
Economic Meal Prep Hacks
Here is a simple trick: buy a whole chicken instead of individual breasts. It is often twice as cheap, and you can use the bones to make a nutrient-rich broth. Focus on frozen vegetables, which are often cheaper than fresh produce and just as nutritious since they are frozen at peak ripeness.
Muscle Recovery Foods: Why Your Diet Doesn’t End at the Gym
The process of building muscle is essentially a cycle of damage and repair. Resistance training creates micro-tears in your muscle fibers. Muscle recovery foods provide the biological tools to stitch those fibers back together, making them thicker and stronger than before.
Anti-Inflammatory Nutrients
Chronic inflammation can slow your progress and lead to overtraining. Foods rich in antioxidants, like blueberries and tart cherry juice, can help manage this. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish or flaxseeds are also potent anti-inflammatories that reduce joint stiffness.
Hydration and Electrolytes
Skeletal muscle is roughly 75% water. Even slight dehydration can significantly reduce your strength and increase your risk of injury. Aim for at least 3 to 4 liters of water daily, especially if you are using supplements like creatine, which draw water into the muscle cells.
Common Muscle Building Mistakes for Beginners
Most beginners fail not because they don’t work hard, but because they fall into common nutritional traps.
Not Eating Enough Calories
This is the number one mistake. Many people are afraid of gaining a little fat, so they stay at maintenance calories. Without a surplus, your body will prioritize basic survival functions over building “luxury” muscle tissue.
Skipping the Post-Workout Meal
Your muscles are most receptive to nutrients in the two hours following a workout. Skipping this window can delay recovery and leave you feeling excessively sore. A simple mix of protein and fast-digesting carbs, like a shake and a banana, is all you need to kickstart the repair process.
Over-Reliance on Supplements
Supplements are meant to supplement a solid diet, not replace it. Focus on getting 90% of your nutrients from whole foods before worrying about which pre-workout powder to buy.
Understanding “Newbie Gains”: What to Expect in Your First Year
If you are new to lifting, you are in a unique physiological position. Beginners often experience a “newbie gain” phase where muscle growth happens much faster than in experienced lifters.
The Adaptation Window
In your first year of smart training and nutrition, men can gain 15 to 25 pounds of muscle, while women can gain 8 to 12 pounds. This is because your muscles are hyper-responsive to the new stimulus of resistance training, causing a massive spike in muscle protein synthesis.
The Plateau Reality
Eventually, your progress will slow down. This is normal. After the first 6-12 months, your body adapts, and you will need more advanced programming and even tighter nutrition to keep seeing results. The key is to build a solid habit during this initial phase so you can push through the inevitable plateaus later.

FAQs: Mastering Your Muscle Gain Diet
How much protein do I actually need to build muscle? For most beginners, aiming for 0.7 to 1.0 gram of protein per pound of body weight is sufficient to support hypertrophy. If you weigh 150 lbs, that means 105 to 150 grams of protein daily.
Can I gain muscle and lose fat at the same time? Yes, this is called body recomposition. It is most common in beginners or those with a high body fat percentage. However, it is a slower process than a dedicated bulking or cutting phase.
What should I eat on my rest days? You should keep your protein intake high even on rest days, as muscle repair happens for up to 48 hours after a workout. You may slightly lower your carbohydrate intake if you are not active, but do not drop below maintenance calories.
Is it okay to do cardio while trying to gain muscle? Yes, cardio is essential for heart health. However, keep it moderate. Too much high-intensity cardio can burn the calories your body needs for muscle building.
Do I need to eat every 3 hours? While not strictly mandatory, eating every 3 to 4 hours helps keep muscle protein synthesis elevated throughout the day. It also makes it easier to hit high calorie targets without feeling overly full.

Conclusion: Taking the First Step Toward Your Gains
Building muscle is a marathon, not a sprint. A well-structured 7-day muscle gain diet plan provides the consistency your body craves to transform. By focusing on a slight caloric surplus, high-quality protein sources, and adequate recovery, you are setting yourself up for long-term success. Don’t let your hard work in the gym go to waste by neglecting your kitchen.
If you are ready to stop guessing and start growing, it is time to get a professional perspective. Our team at Diet Dekho can help you fine-tune your macros and create a sustainable plan tailored to your unique body type and goals.
Ready to transform your physique? Fill out our assessment form here and let’s build your custom roadmap to success!
BOOK YOUR APPOINTMENTAbhinav is the Founder of Diet Dekho, helping people manage weight and lifestyle health through simple, practical nutrition and personalized diet plans.
