Introduction
Fatty liver disease is a silent epidemic. It is now one of the most common health issues worldwide. The normal characteristics are excessive accumulation of fat in liver cells. The silent progression of the condition may result in serious health complications. Despite its prevalence, fatty liver disease remains underdiagnosed and misunderstood. It often progresses to more severe stages before detection.
This is a guide on tackling the hidden dangers of fatty liver disease. It explains how early intervention and proactive management can help. This blog provides a detailed plan to combat fatty liver disease. It covers regular screening, lifestyle changes, medical management, and new treatments. Acting early on the risks may guard liver health. It may improve life quality and reduce suffering from this disease.

Table of Contents
Take action: Prevention and Management
Fatty liver disease has silent dangers. They stress the need for early intervention and proactive management. Listed here are the major steps:
1. Regular Screening
At-risk patients, especially the obese, diabetics, and heavy drinkers, must be screened for fatty liver disease, as they are at high risk. So, they need regular tests. Blood tests, imaging studies, and tests of hepatic function will help in its early detection. An early diagnosis will allow timely interventions. They help stop or reverse the disease.
Screen high-risk groups: metabolic syndrome patients, type 2 diabetics, and those with a family history of liver disease. Noninvasive tests, like transient elastography and serum biomarkers, can improve screening. They are more efficient and boost patient compliance.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
A healthy lifestyle is key to preventing and controlling the disease. It requires a balanced diet of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. It also needs some moderate exercise. A weight loss of 5 to 10 percent can greatly reduce liver fat and improve liver function.
The Mediterranean diet is a specific diet. It benefits patients with NAFLD. This diet is high in healthy fat, fiber, and antioxidants. It reduces inflammation and boosts metabolic health. Aerobic exercise, resistance training, and activity improve insulin sensitivity. They also help with weight loss. This simplifies life for patients.

3. Medical Management
For people with fatty liver, treatment may involve drugs for diabetes, cholesterol, and blood pressure. New drug research aims to reduce fat in liver cells. It also seeks to decrease liver inflammation and scarring. These newer treatments, like GLP-1 receptor agonists, show promise for better liver health. So do SGLT2 inhibitors and PPAR agonists.
Healthcare providers should tailor treatments based on the patient’s risks and disease stage. Care from a team of hepatologists, endocrinologists, and dietitians can improve outcomes. It can also better manage related health issues.
4. Avoid alcohol
There should be a reduction or complete avoidance of alcohol, especially in AFLD patients. Even moderate drinking can worsen NAFLD. Those with alcohol use disorders, can get help. Counseling and support programs can help them achieve and maintain sobriety.
Abstinence from alcohol is essential in arresting AFLD. Patients must learn about alcohol’s harmful effects on the liver. They must receive resources for support to achieve sobriety and treat addiction.
5. Follow-up Care
There is a need for follow-up to adjust the needful treatment plan with health providers on the liver’s health. A deep test of liver function, fibrosis, and metabolism will help doctors make decisions as the disease progresses. It will also prevent further disease progression.
Patients with advanced liver disease need careful management. It must check for complications, such as variceal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy, and liver cancer. Patients do better with care based on guidelines for treating and preventing cirrhosis. These guidelines are based on evidence.

New Treatments and Research
Several new treatments and therapies are under study, which relate to this disease. The areas with potential are in research on medications. Several drugs are under study to decrease liver fat, inflammation, and fibrosis. These include the GLP1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors, and PPAR agonists.
1. Nutraceuticals
Nutraceuticals, like omega-3s and vitamin E, may help with fatty liver disease. They are being tested for this. More recently, research in the use of probiotics is also contributing. A related, emerging field is nutrigenomics. It studies genetic variations in response to a diet. This could allow for personalized diet advice for patients with fatty liver disease. It would tailor nutritional therapy to each person’s genetic profile.
2. Gut Microbiome
Studies are underway on gut microbiome interventions for liver health. These include probiotics and prebiotics. Modulating the gut microbiome may reduce liver fat, inflammation, and fibrosis. So, it may be a new way to manage fatty liver disease. Fecal microbiota transplantation is under exploration for its potential as a therapy. Early studies suggest that changing gut bacteria may improve metabolic health. It could also reduce fat in the liver.
3. Genetic Research
Genetic research has found the variants that predispose people to fatty liver disease. Genetics can help develop targeted therapies and personalized medicine. Genotypic markers associated with disease progression will permit risk stratification with early interventions. Researchers are studying gene editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9. They may treat fatty liver disease with them.
4. Lifestyle Interventions
Researchers are testing new diets, like intermittent fasting, for their effects on liver health. Such diets improve insulin sensitivity, reduce liver fat, and aid weight loss. Including behavioral and psychological support in lifestyle changes may boost adherence. It may also improve long-term success. These include mindfulness-based interventions and cognitive-behavioral therapy. They are being studied for their effects on eating and long-term lifestyle changes.

Dietary Intervention and Diet Plan
Dietary intervention is the key to managing and reversing fatty liver disease. A balanced diet, low in unhealthy fats and sugar, is key to good health and a healthy liver. One effective diet would be the Mediterranean diet. This diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats through olive oil. It is well-known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. So, it reduces liver inflammation and improves metabolic health. Increased intake of fiber-rich foods, like legumes and whole grains, is important in managing fatty liver disease. It helps with weight and improves insulin sensitivity.
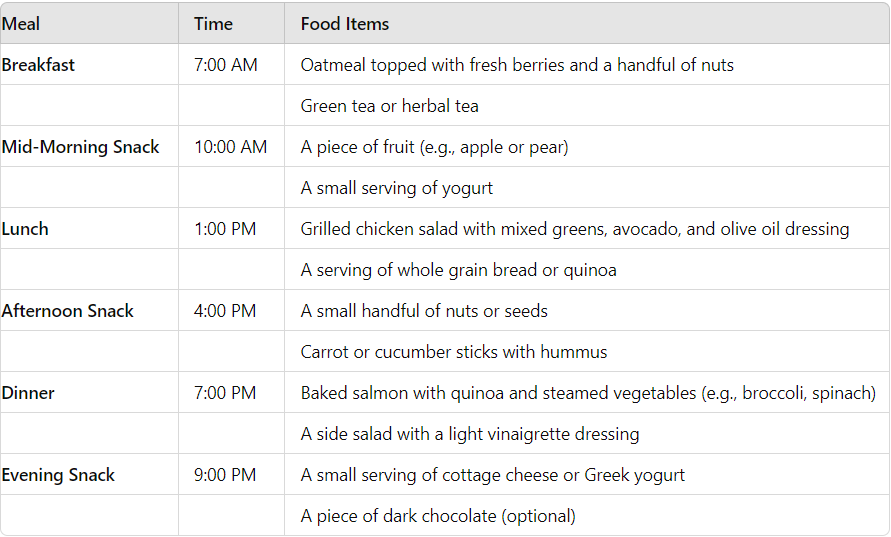
Below is a sample diet plan:
Akansha: from diagnosis to victory, her journey of transformation.
A chirpy 23-year-old girl, Akansha, was diagnosed with Fatty Liver Grade 2. Her doctor recommended her to make some serious lifestyle changes if she wanted to manage her condition. Moved by the urge to take back control of her body, Akansha started a life-changing journey with DietSpeed.
When Akansha started, her weight was 63.5 kg. The challenge was huge, but she never lost hope. She was very serious about the nutrition program provided to her. She took only healthy foods that were nourishing for her body and favorable for her health. At the same time, she started a diet. She also took up yoga. She attended classes and did home practice.
Her journey was anything but smooth. She was constantly running away from the diet and most mornings yoga seemed more challenging than ever before. But Akansha never lost her determination. She kept her eyes on the prize, reaffirming the goal.
And it was only after a month of religiously following Diet Speed that Akansha started to see results. It showed what discipline and patience the process demanded, as she lost 7.5 kg. Her fatty liver improved. She felt more energetic and optimistic. Her improved health and well-being became visible.
Soon, Akansha’s story inspired those around her. She walked on, full of passion and dedication. She aimed for not just a healthier weight, but a happy, vibrant life. Her story is of the kind that shows if one has the right mindset and support, then he or she can achieve his or her health and wellness targets.

Conclusion
It is a silent epidemic. It risks liver and heart health, and quality of life. Awareness of these risks, and proactive measures, can protect liver health. They can also reduce this common burden. Public health initiatives, education, and research are key to tackling the rise of fatty liver disease. They can help millions worldwide.
A comprehensive approach to management of fatty liver disease must incorporate mental and emotional support. Apart from the positive effect on quality of life, addressing psychological well-being enhances interventions that focus on physical health. The individuals can successfully go through their journey if they create a supporting environment, seek help when needed, and regularly engage in mind-body practices to be resilient and positive while experiencing improvements in health that are sustainable.
Fatty liver disease needs a team approach. It requires a change in lifestyle, medical care, and close monitoring. New therapies and research may relieve suffering from this disease. Early detection, personalized treatment, and quality care can help. They enable health personnel to manage liver fat disease. This can lead to the best quality of life for patients. If people unite in these efforts, they can contain the silent dangers of fatty liver diseases. This would open a path to a healthier future.
BOOK YOUR APPOINTMENTAbhinav is the Founder of Diet Dekho, helping people manage weight and lifestyle health through simple, practical nutrition and personalized diet plans.
